Last Updated on July, 2024
Peripheral Neuropathy affects the peripheral nervous system. The brain and spinal cord are affected by this disease which causes damage to sensory nerves.
The symptoms of peripheral Neuropathy are not challenging to spot. If you suffer from any of these symptoms, it is best to seek professional guidance and diagnosis.
The disease affects the central nervous system, and both the brain and spinal cord are affected. The central nervous system loses its ability to effectively send signals to various body parts. This is caused by nerve damage, which resultantly causes pain and agony.
The peripheral nerves, which rest outside the brain and spinal cord, are damaged by this disease, which leads to a lack of effective communication between the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
This article will elaborate on the various signs and symptoms of this illness and provide you with ALL the information you need to BETTER understand the condition.
Quick Summary
Early warning signs of Neuropathy include numbness, tingling, and burning/shooting pain in the hands and feet that can spread upwards to the legs and arms.
Risk factors for Neuropathy include rheumatoid arthritis, vitamin deficiencies, old age, alcoholism, and smoking.
Diagnosis for Neuropathy includes nerve biopsy, muscle and nerve ultrasound, and clinical assessment. Early diagnosis is essential to prevent the condition from worsening.
Quick Navigation
- What is Neuropathy?
- Types of Neuropathy
- What are the Warning Signs of Neuropathy?
- Symptoms and Signs of Neuropathy
- Common Questions About Neuropathy
- What are the Causes of Neuropathy?
- What are the Risk Factors?
- Neuropathic Pain Explained
- Stages of Neuropathy
- What is the Diagnosis of Neuropathy?
- How to Prevent Neuropathy?
- Is Neuropathy a Serious Problem?
- Final Thoughts
- FAQs
- How Long Does Neuropathy Last for?
- Can Neuropathy be Treated?
- Does Neuropathy Cause Amputation?
- How Do You Detect Neuropathy?
- Can Neuropathy Affect More Than One Part of the Body?
- Was this article helpful?
What is Neuropathy?

Plain and simply put, Neuropathy, also known as peripheral Neuropathy, affects the peripheral nervous system. It happens when a nerve or a group of nerves in your body doesn’t function properly.
Peripheral nerves reside outside the spinal cord and brain. These peripheral nerves are an essential part of the central nervous system.
Nerves are sensitive, and this sensitive nature brings about the complications of Peripheral Neuropathy. Even minor damage to a nerve can have severe effects on health and well-being.
Peripheral Neuropathy predominantly affects the sensory nerves of the body, leading to loss of sensation and feeling. Peripheral Neuropathy often accompanies pain and numbness, and muscle weakness is a common trait of the illness. (1)
Autonomic nerves that are damaged can lead to disastrous effects on the body, which is usually what happens with peripheral Neuropathy. The neuropathic pain involved in the movement of the body part affected by nerve damage makes it very difficult for people to perform basic tasks such as moving the body part or even walking.
Though infectious diseases can cause peripheral Neuropathy, the condition itself is not contagious.
Though nerve regeneration is a likelihood with the proper diagnosis, the illness affects the nervous system, brain, and spinal cord, which will become difficult to manage without proper treatment.
Types of Neuropathy
There are mainly four types of Neuropathy, classified based on the types of nerves this condition affects.
MOTOR NEUROPATHY is caused when the motor neurons are affected by nerve damage. Similarly, SENSORY NEUROPATHY results when the sensory nerves are affected by the condition.
MOTOR-SENSORY NEUROPATHY affects both the sensory and motor nervous systems, usually resulting in more damage and a more substantial need for treatment and diagnosis.
Fourthly, there is AUTONOMIC NEUROPATHY which affects the whole autonomic nervous system.
Apart from these four main types of classifications of this illness, there are also other types of Neuropathy, such as Chemotherapy Induced Neuropathy, also known as Chemotherapy Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. As the name suggests, this type of Neuropathy is caused by chemotherapy.
When no specific cause can be identified, the illness is termed Idiopathic Neuropathy.
Other types of Neuropathy include Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy, a chronic form of Guillain-Barre in which the symptoms continue for months and even years.
Diabetic Neuropathy (Diabetic Polyneuropathy) is another type of Neuropathy. Diabetic Neuropathy is caused as a resultant effect of diabetes. People who suffer from diabetes have a greater chance of developing Diabetic Neuropathy.
When you take a Peripheral Neuropathy fact sheet, you will notice that all these varieties of this common illness have one common factor: nerve damage.
What are the Warning Signs of Neuropathy?
Early warning signs of Neuropathy primarily include numbness. Neuropathy affects the sensory and motor nerves, resulting in weakened nerve health.
Medical conditions such as diabetes, alcoholism, or rheumatoid arthritis are all warning signs of Neuropathy, especially if they are accompanied by prickling numbness or tingling in the feet and hands, which spread upwards to your legs and arms.
Burning and sharp pain can also be a telltale sign that your nervous system may be suffering.
Autoimmune diseases such as Neuropathy will make you extremely sensitive to touch. This is because the sensory nerves that may be affected by the illness cause your touch to be EXTREMELY sensitive.
These are all warning signs for Neuropathy, which should help you detect the illness at its early stages. There are many causes of peripheral Neuropathy, and the best action is to act fast when these warning signs appear.
Specifically, for diabetic Neuropathy, high blood sugar levels are a warning sign that Neuropathy could result from diabetes.
Pain signals are a clear sign that something is wrong. Though the symptoms depend on a host of factors, including the type of Neuropathy, the warning signs are all the same.
If you suspect damage to a peripheral nerve or autonomic nerve damage, it is BEST to get a proper diagnosis to ensure proper treatment can be attained.
Symptoms and Signs of Neuropathy
Regardless of the type of Neuropathy, the signs and symptoms experienced are similar. Neuropathy can be a condition that develops as a result of other conditions that you may suffer from, such as chronic liver disease or kidney failure.
However, the symptoms and signs of Neuropathy broadly involve numbness and pain. With the condition primarily affecting the feet and hands, one of the first signs and symptoms that you will notice is numbness and tingling in the feet and hands.
This can be followed by a burning, stabbing, or shooting pain, which could affect the areas where the nerve damage is prominent. A damaged peripheral nerve itself can lead to such signs and symptoms.
Peripheral Neuropathy may also cause you to lose balance and coordination. Loss of balance is caused by peripheral nerve damage because it affects the central and autonomic nervous systems.
Nerve tissue damage can cause your muscles to become weak, especially in the feet, and can affect your motor nerves, leading to motor symptoms such as twitching and muscle cramps.
Neuropathy symptoms are not difficult to detect. If you suffer from neuropathy symptoms, you will notice all these signs one by one, if not all at once.
Other symptoms include thinning of muscles and difficulty in moving the affected body part (leg or arm.)
Neuropathy can affect nerves that control muscle movement. Not only will it become difficult for you to move, but you will also be EXTREMELY sensitive to touch.
Common Questions About Neuropathy
When it comes to Neuropathy, there are some common questions that you should ask to keep yourself informed about the condition.
For instance, you should ask the question of what causes Peripheral Neuropathy? Does kidney disease or metabolic disorders leave room for developing Neuropathy? It is essential that you understand that Neuropathy can develop as a resultant effect of many illnesses.
It would help if you also familiarize yourself with the common symptoms. As mentioned above, numbness and pain are the most commonly associated symptoms of Neuropathy. This is because the illness affects nerve function.

What is the diagnosis for Neuropathy and what can be done about the pain are just questions you should be asking. Further to this, you may also want to know of the adverse side effects of any of the prescription medication that is used in the treatment of this condition.
With treatment in mind, another common question you should inquire about is the alternative courses of treatment and how you can manage the illness at home with home remedies.
Asking these common questions will give you a better idea about different kinds of peripheral neuropathies that stem from various causes.
What are the Causes of Neuropathy?
Primarily, Peripheral Neuropathy is caused by nutritional or vitamin deficiencies. Apart from this, alcoholism and exposure to toxins can lead to nerve damage in the peripheral nerves.
Muscle weakness is a general sign of Neuropathy; the condition is hastened by bad diet and alcohol. If you suffer from muscle weakness or see early signs of Neuropathy, it would be the best time to quit consuming alcohol and ensure you maintain a better diet.
Additionally, damaged autonomic nerves cause peripheral neuropathy symptoms due to various other medical conditions such as bone marrow disorders, blood pressure, kidney disease, Charcot Marie Tooth disease, ulnar nerve palsy, tumors, diabetes, and infections, to cite a few.
Ulnar nerve palsy, for instance, occurs when the nerve on the surface of the skin at the elbow is damaged. Charcot Marie Tooth disease (CMT) is a condition that affects a group of peripheral nerves, which incur further nerve damage due to peripheral neuropathies.
Severe pain is a resultant effect of an undiagnosed condition; even injuries and accidents that may have happened can lead the way to neurological disorders such as Neuropathy.
Neurological disorders affect nerve health, and arise when motor nerves, for instance, cannot perform and function correctly. With the causes of Neuropathy being so many, it is essential that we understand this condition as much as possible to treat the condition better.
What are the Risk Factors?
Illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases are all risk factors for Neuropathy. Rheumatoid arthritis can cause severe, UNBEARABLE pain associated with the pain of Neuropathy.
If you suffer from a condition known to lead to peripheral Neuropathy, including vitamin deficiencies, the risk factor of developing this illness is greater.
Vitamin deficiencies are something that you may not directly link to Peripheral Neuropathy.
However, did you know that vitamin deficiencies are one of the leading causes of developing this condition in old age?
Other factors, such as old age, could also lead to chronic neuropathic pain.
Furthermore, habits such as alcoholism and smoking are also known to affect the health of nerves, which are considered risk factors for Peripheral Neuropathy.
Though the type of Peripheral Neuropathy varies based on the cause, the risk factors are similar.
A weak immune system could mean you are more susceptible to infections, which is also a cause of Neuropathy. Hence, a weak immune system is also a risk factor.
High blood sugar levels can be a sign of diabetes. The trouble with high blood sugar is that it slowly works to eat away the functioning of nerves, resulting in Diabetic Neuropathy.
The health of the spinal cord is also crucial in understanding the risk factor for the health of peripheral nerves. The healthier of a spinal cord you have, the healthier your peripheral nerves will be.
Anything that has the chance to damage your peripheral nerves, including chemotherapy, can lead the way to develop Neuropathy.
Neuropathic Pain Explained
With peripheral neuropathy symptoms including pain and numbness, Peripheral Neuropathy is commonly associated with the pain, also known as neuropathic pain, which the patient experiences.
Peripheral Neuropathy symptoms include neuropathic pain, a sharp, burning, and intense type of pain.
Though the pain levels may be lower at the onset of the condition, when left untreated, it could lead to the development of EXTREME pain, making it difficult for you to move.
Neuropathic pain is one of the symptoms of peripheral Neuropathy; various things can be adopted to help better manage pain.
Painkillers being the remedial means of treating this illness, there are better means of managing neuropathic pain, which involve the diagnosis of Peripheral Neuropathy.
Stages of Neuropathy
There are four main stages of this illness. The first stage includes pain and numbness, which was mentioned as an early sign of Neuropathy.
General pain in the movement of the body part and numbness is stage one and is the earliest possible sign of the illness. It is best to spot the issue at an early stage and get the necessary diagnosis to ensure that the illness does not get difficult to manage.
When left untreated, Neuropathy (Peripheral Neuropathy) can lead to constant pain, which doesn’t go away. This is considered the second stage of this illness. At this stage, the patient will be experiencing constant pain, which may become difficult to manage.
Even if the illness was not correctly detected in stage one, in stage two, it might become more evident to the patient that they may be suffering from Neuropathy.
Stage three involves the intensification of the pain. The pain becomes more severe, and moving affected limbs becomes problematic. Basic tasks such as walking or brushing your teeth will become difficult at this stage. As the pain intensifies, it will become more evident that proper care and diagnosis are necessary to combat the effects of the illness.
Lastly, in stage four, the patient will experience complete numbness and loss of sensation. Apart from a heightened sensitivity, experiencing complete numbness will make it difficult to move the affected body part. If not properly diagnosed, it could lead to infection and the possible need for AMPUTATION.
These are the four stages of Neuropathy. Considering that in the fourth stage, it could lead to amputation, it is essential that you try to detect this condition in the earliest stage possible, so proper care can be attained to ensure better management of the condition.
What is the Diagnosis of Neuropathy?
A nerve biopsy will tell you the extent to which damage to nerves has occurred. In order to diagnose Peripheral Neuropathy (before addressing peripheral neuropathy treatments), the exact cause and the type of Neuropathy will have to be deduced.
A muscle and nerve ultrasound can often be relied upon to understand the damage to the nervous system.
How is Peripheral Neuropathy diagnosed, you may ask? The first thing physicians do is try to understand the condition based on the patient’s medical history. A neurologist will conduct a clinical assessment to understand the patient’s symptoms through a physical examination.
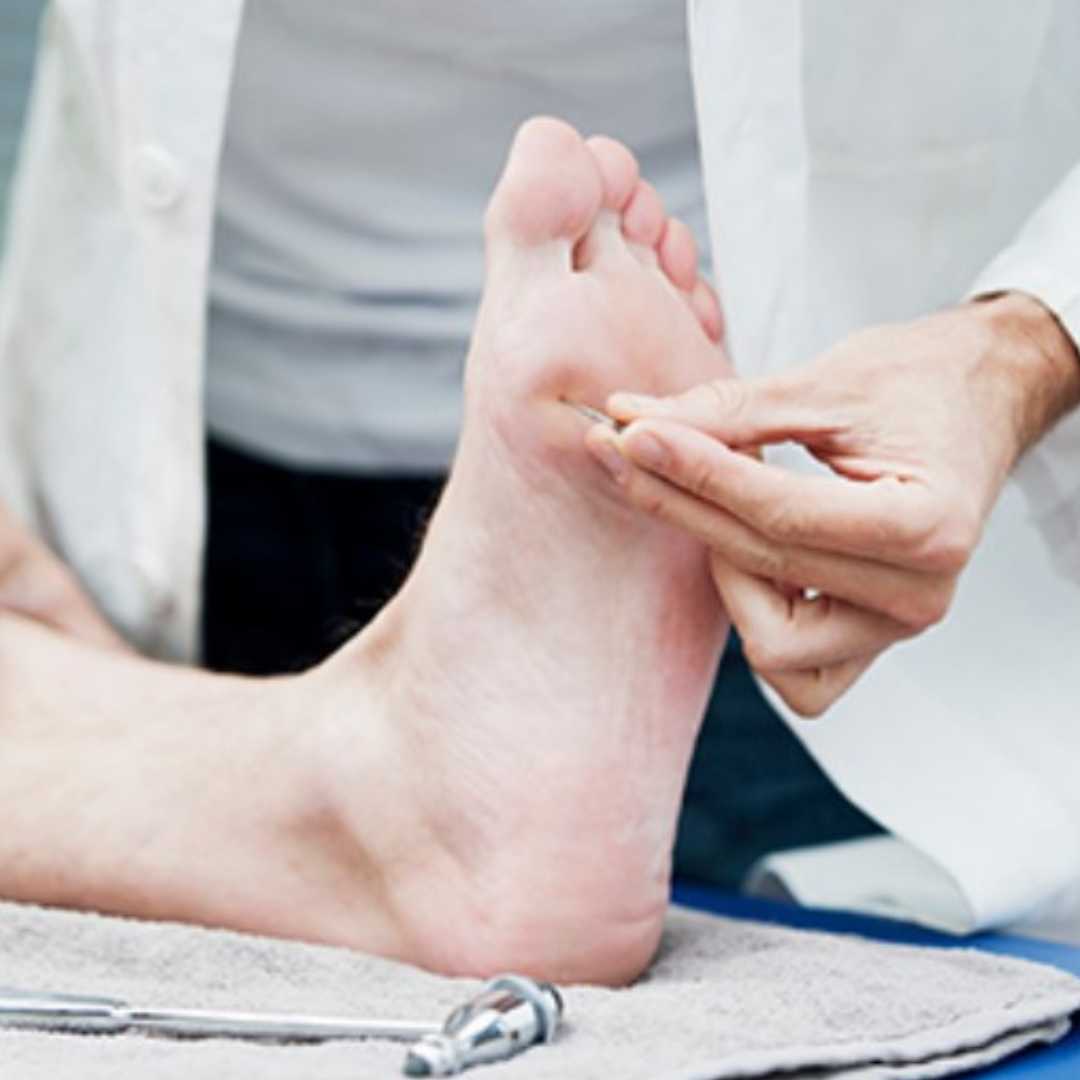
If you notice stage one of Neuropathy, it is best to get a proper clinical assessment early.
Medications in treating Neuropathy vary based on the type of Neuropathy, the stage of Neuropathy, and other underlying conditions. Amitriptyline, Duloxetine, Pregabalin, and Gabapentin are all prescribed based on need and type of Neuropathy.
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is used to attempt nerve regeneration and better manage pain. It is considered an effective treatment in the fight against Neuropathy. Though the effectiveness of this treatment hasn’t been confirmed for patients with Neuropathy, it has been considered a valuable means of better-managing pain.
How to Prevent Neuropathy?
Nerve pain is the resultant cause being Neuropathy, and preventing it includes better care for the nervous system.
Regular exercise and eating a diet loaded with nutrients, including essential minerals and vitamins, will help you prevent this condition. Better overall health is what is necessary for the prevention of this disease. This means eating healthy meals and getting plenty of exercise to keep your body in optimum shape.
Apart from a good diet and exercise, which are essential parts of prevention, avoiding toxins in the diet that can lead to nerve damage is another factor. You don’t want to consume a diet that is high in sugar, as this could lead to the development of diabetic Neuropathy.
Further to this, you don’t want to consume foods that contain toxins because the build-up of toxins could lead to the damage of nerves, thereby leading to Neuropathy.
Avoiding alcohol and smoking are both essential in preventing damage to nerves. Both smoking and the consumption of alcohol have been linked to nerve damage. Extensive use of alcohol could have disastrous effects on health, including damage to the nervous system.
What is essential to note is how difficult it is to fix damaged nerves. Nerve damage isn’t the easiest thing to fix. Nerve regeneration is slow, and damaged nerves are usually difficult to restore. As a result, prevention is the best cure, and you should do everything you can to stay healthy to prevent Neuropathy from causing havoc in your life!
Is Neuropathy a Serious Problem?
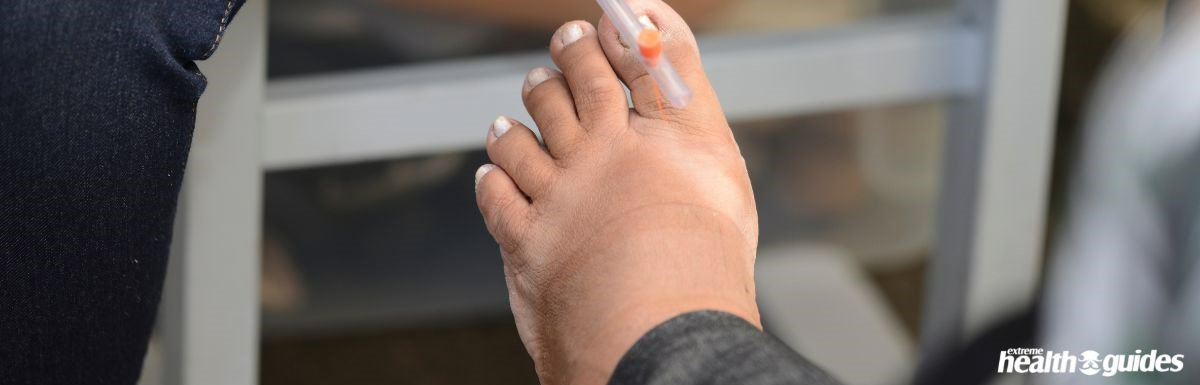
When left untreated, Neuropathy in the late stage could lead to the complete inability to move a body part (arm or leg.) This would make it very difficult for you to further basic tasks such as brushing your teeth or walking.
The complete numbness experienced by people in the later stages of this disease drastically affects their quality of life and well-being. Imagine no longer being able to lift your arm or move your hand.
To understand the severity of Neuropathy, you must first understand that patients with late stages of this illness cannot feed themselves or move and lose complete autonomy over their bodies.
Considering how late-stage Neuropathy can lead to amputation, it can be established with a great deal of AUTHORITY that Neuropathy is a very serious problem, which may have drastic effects on the lives of patients suffering from the condition.
Final Thoughts
Neuropathy is a condition that may seem like not much of a problem in the early stages of the illness. However, during the later stages of the illness, the complications concerning the condition get more severe.
Though the pain experienced will be bearable during the early stages, in later stages, the pain associated with Neuropathy makes it difficult for patients to live a regular life.
Imagine not being able to use your hands and legs, and you will understand the seriousness of the condition.
As recommended, it is best to detect this condition in the earliest stage possible and seek professional guidance and treatment to ensure that you diagnose it in the early stages. When detected in the early stages, nerve damage can be halted, thereby preventing extreme pain from affecting patients’ lives.
This article was intended to provide you with all the information you need to understand Neuropathy better. We hope you found this article informative and helpful in battling this crippling condition.
FAQs
Was this article helpful?
Was this article helpful?